
Diseases caused by the human papillomavirus have been known for a very long time. First of all, these are all types of warts, from which every sixth person on the planet suffers. However, the pathogen itself has attracted the attention of scientists only in the last 30-40 years. The group of human papillomaviruses (Human Papillomavirus - HPV) was identified as a separate species in 1971. Since then, scientists have classified HPV types and established their relationship with many pathologies, but research is still ongoing. At the same time, doctors are looking for more effective ways to fight this insidious virus.
What is HPV?
Human papillomavirus is a large group of DNA-containing viruses that exhibit an affinity for the epithelial cells that form the skin and mucosa. Today, about 170 types of the virus have been discovered and about 60 have been well studied.
Some papillomaviruses are dangerous because of their oncogenic activity, that is, they increase the risk of the formation of malignant tumors. Since the 1980s, research has been conducted that has proven that human papillomavirus infection plays a role in the development of adenocarcinoma and squamous cell cancer of the cervix (the second type of tumor is much more common). In 99% of cases, oncology patients are diagnosed with HPV infection and cells specifically modified by the virus.
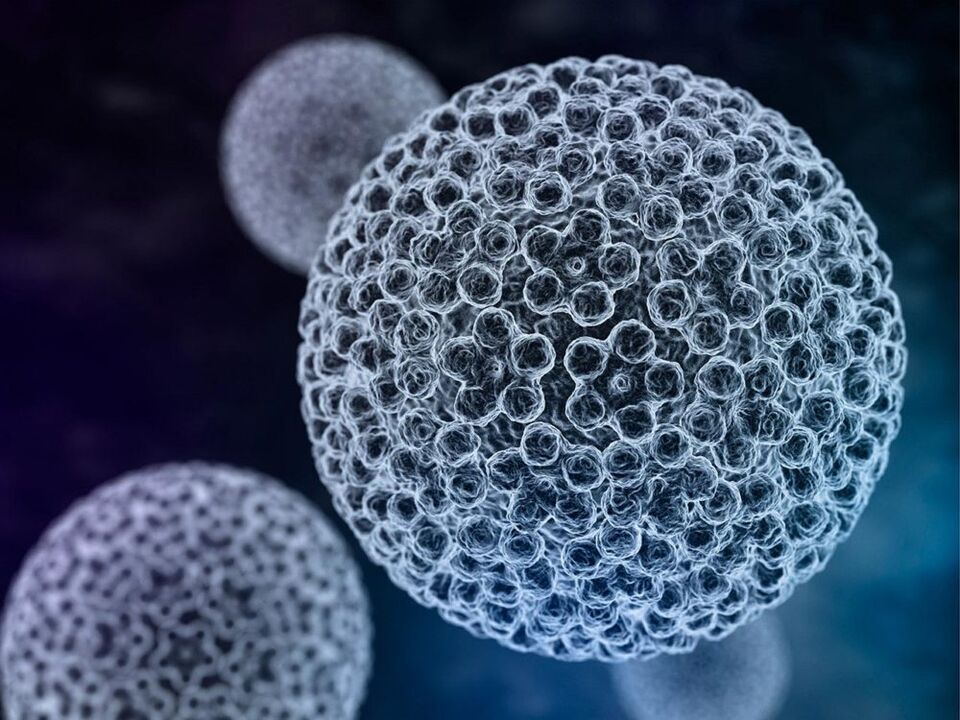
The papilloma virus invades epithelial cells. After its penetration into the genome, reproduction (reproduction of the DNA of the virus) begins. In this case, the cells divide atypically, and their structure changes, which can be seen if you do a cytological analysis.
The papilloma virus manifests itself in specific changes in the epithelium:
- on the skin of the body (vulgar and flat warts, papilloma);
- in the epidermis and mucous membranes of the genital organs (genital warts, bowenoid papulosis, cervical neoplasia, cancer);
- in the mucosa of other organs (oral cavity, larynx, bladder, rectum, bronchi, etc. ).
Changes in the first group are caused by non-oncogenic viruses. They are uncomfortable, but not dangerous. The third group of manifestations is considered atypical and is recorded relatively rarely.
All types of viruses are divided into three groups:
- with low oncogenic risk (3, 6, 11, 13, 32, 40, 41, 43, 44, 51, 61);
- with moderate risk (30, 35, 45, 52, 56);
- high risk (16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 59, 64).
Common types 6 and 11 cause multiple anogenital warts and benign cervical neoplasia. Their discovery in a pregnant woman requires attention, as there is a risk of developing laryngeal papillomatosis in a newborn after contact with the mother's mucous membrane during childbirth. Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, women and men should undergo an HPV test.
The detection of viruses from the third group in the analysis results requires special attention, as the risk of tissue degeneration is high and the patient requires advanced diagnosis.
Methods of infection
The most common route of infection is sexual. Almost all sexually active adults are diagnosed with HPV. However, most often the infection is transient - the body copes with it, and after a year and a half the virus is not detected in tests. Only occasionally does HPV cause minor clinical manifestations and, in extremely rare cases, cancer, which develops many years after infection (10-15).
Other routes of infection:
- CONTACT– through touch. This is how you can get infected with warts;
- Local.The virus remains stable in the external environment for some time. Infection is possible in a bathroom, swimming pool and other public places. The pathogen penetrates through microdamages in the skin.
- Vertical.The virus can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth. In this case, the newborn occasionally develops papillomatosis of the larynx and upper respiratory tract. In some cases, the baby is affected by genital warts.
- Autoinfection.Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection can spread throughout the body from one place to another, for example, by shaving or scratching warts.
Stages of development of infection
After infection, the latent phase begins - latent or carrying PVI. At the same time, the virus is inactive, does not manifest itself clinically and is not detected during cytological and histological examination, since it does not reproduce its copies and does not change the epithelial tissue. However, its DNA can be detected using PCR analysis.
Important!
It is not at all necessary for the latent phase to develop into disease. Perhaps the person himself will remain only a carrier and he will not have clinical manifestations.
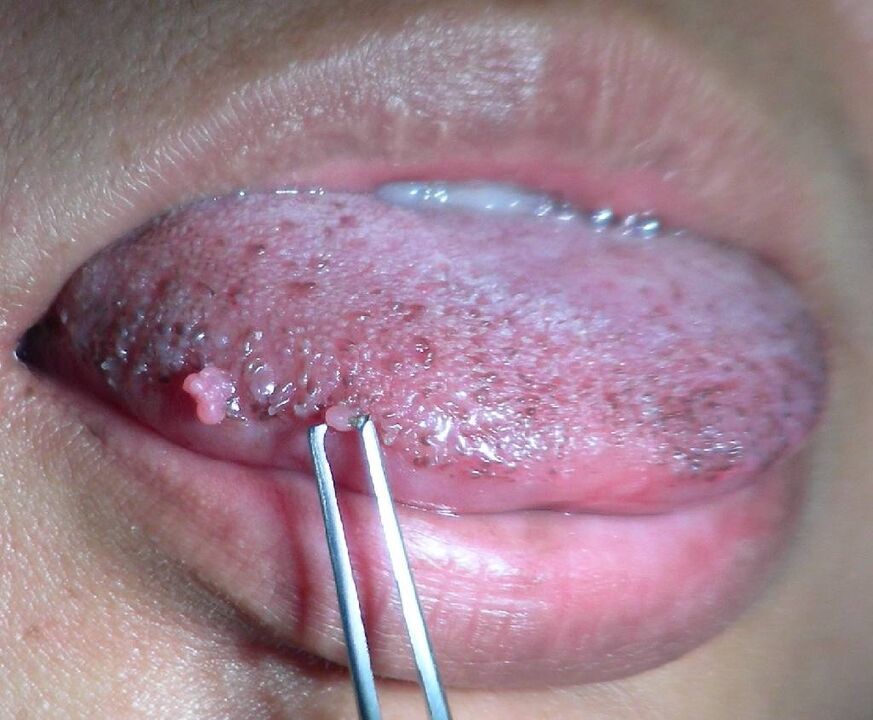
In the second stage (subclinical), tissue changes have already begun, but they may still be minimal and not bother the person. However, when taking a cytological analysis, atypical cells are detected, and after the examination, single condylomas or small papillomas can be seen.
The third stage is clinical (manifest). The symptoms are pronounced and the disease requires treatment. Most often, PVI occurs latently or subclinically, and visible signs appear under the influence of provoking factors.
The fourth stage (mutagenesis) is a sad consequence of PVI. During this period, the cells become malignant and the carcinoma begins to grow.
Causes of papillomavirus activation
PVI infection occurs very easily, but the human immune system copes well with it, and often the virus disappears on its own. A persistent infection that periodically worsens and does not leave the body is a sign of a reduced immune response.
The following factors contribute to this:
- Age. Healthy adults are less likely to suffer from PVI. Most often - children, teenagers and the elderly;
- Long-term chronic diseases that weaken the body;
- Endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases) and hormonal fluctuations (pregnancy, menopause);
- Continuous stress, prolonged psycho-emotional stress;
- Poor nutrition, strict diet, lack of vitamins, minerals and complete proteins;
- Severe dietary obesity and a sedentary lifestyle;
- Taking medications that suppress the immune system, exposure to radiation, chemotherapy;
- Primary and secondary immunodeficiency, HIV;
- Initiation of sexual activity before the age of 16 and intimate contacts without discrimination;
- Co-infection with other sexually transmitted infections;
- Gynecological procedures that lead to mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the cervical canal (abortion, curettage, installation of a coil, etc. ).
The incubation period for PVI is highly variable. The pathogen can remain in a latent, inactive state for a long time (from 3 weeks to several years), so it is impossible to accurately determine the time and circumstances of infection. A person can be infected with several types of the virus at the same time and be repeatedly reinfected, for example, from a sexual partner.
HPV diagnosis
The first stage of diagnosis is always an examination by a doctor and the collection of anamnesis. Women are examined by a gynecologist, men by a urologist or dermatovenerologist. When exophytic genital warts are detected, the diagnosis is obvious, since these neoplasms are characteristic only of PVI.
Acetic acid test
If the disease is in a subclinical stage, small condylomas may not be visible visually. Therefore, a test with acetic acid is carried out - after treatment with it, new growths become white and stand out against the background of the surface.
The same thing happens with the cervical mucus (examined by colposcopy) - the identification of white areas in it indicates that the epithelium in this place has changed. It is from this surface that a cytological smear is taken or a biopsy is performed.
If the acetic acid test is positive, observation and control is required after six months, as the disease may progress. On the other hand, the virus can go into a latent state, then the manifestations will disappear.
Schiller's test
It is performed as part of an extended colposcopy after an acetic acid test. In this case, the areas of the fabric previously treated with vinegar are painted with a solution of iodine in glycerin. Normal cells absorb this solution and turn a uniform brown color. In atypical cells, glycogen accumulation processes are interrupted and they do not absorb the solution. Mosaic coloring occurs, its characteristic features suggest a diagnosis.
Cytological smear
It is also called the PAP test after the name of its inventor, the Greek doctor Papanikolaou. For testing, a scrap is taken from the cervical mucosa (urethra in men) to obtain epithelial cells for analysis. The biomaterial is applied to a glass slide, fixed with alcohol, stained and examined under a microscope.

The interpretation of the results is done by the doctor, as other data are also taken into account: cytology results, PCR analysis, tests for other infections, the presence of inflammation in the vagina, etc. The result of class 1-2 is considered negative, that is, no morphological changes caused by the virus were detected.
For grade 3, additional examination methods are prescribed, but grades 4 and 5 are a possible sign of grade III neoplasia or cancer.
PCR analysis
A highly sensitive test that detects the presence of viral DNA in epithelial cells. The study can be performed with the same biomaterial that was taken for cytological analysis. The polymerase chain reaction is carried out in a special device, where a predetermined gene sequence is copied many times.
The PCR method is used to detect latent sexually transmitted infections, which include HPV, so it is used as part of a screening examination. Genital warts often appear against the background of other venereal diseases. If positive PCR results are obtained, an in-depth diagnosis is required.
Because the DNA test is so accurate, its use often leads to overdiagnosis. After all, the detected DNA of a virus does not mean that a person is sick. It could be a new infection that will go away on its own.
Therefore, the PCR test is expanded - a quantitative analysis is performed to detect the concentration of the pathogen in the tissues, that is, the viral load (indicated in the results with the letters lg). At the same time, genotyping is performed to determine the exact type of pathogen. If oncogenic strains are found, control tests are prescribed after 3-6 months.
Digene test
This method is screening (primary, performed for initial diagnosis). It also detects viral DNA in tissue. In this case, the oncogenicity of viruses and their number are determined collectively. The Digene test in combination with a cytological test is the accepted standard today in many developed countries for the identification of clinically significant HPV infection and cancer risk.

Histological examination
This is an advanced diagnostic method. It is prescribed to a woman when positive screening results are obtained: the cytological analysis showed a 3-4-5 class of cells. A piece of tissue obtained as a result of a biopsy is examined under a microscope.
The study allows us to identify cells specifically modified by the virus - koilocytes and dyskeratocytes, as well as cells with malignant signs. Thus, histology makes it possible to determine the degree of neoplasia and identify cancer in the early stages, when it can be treated successfully.
In some cases, tissues obtained from neoplasms of the skin and mucous membranes are submitted for histological analysis if there are doubts about their nature and good quality.
Treatment of PVI
In the latent phase of PVI, no treatment is required. Detected infection becomes only a reason for observation over time. It is worth noting that it is impossible to kill the virus in the body with drugs, since it replicates inside the cells.
An infected person is advised to:
- avoid factors that reduce immunity, take vitamins;
- recover from concomitant sexually transmitted infections, if detected, do not develop chronic diseases;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits;
- live a sex life with a permanent and trusted partner.
Treatment of human papillomavirus begins with the stage of subclinical manifestations. At this stage it is conservative. Immunomodulatory therapy is usually prescribed. For this purpose, preparations of human interferon or its inducers are used.
Nonspecific immunomodulators are also effective against HPV. Antiviral drugs are used.
Doctors often prescribe local medicines at the same time - ointments, gels and creams.
Important!
Immunomodulatory treatment is prescribed only by a doctor based on the results of an immunogram; uncontrolled use of drugs can lead to the opposite result - a malfunction of the immune system.
In the third stage, radical methods are included in the treatment regimen. You can get rid of genital warts, papillomas and warts using the following methods:
- chemical removal with cauterizing drugs;
- radio knife;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser destruction;
- cryodestruction.
The same methods are used in the treatment of benign cervical pathologies.
Surgical removal of tissue is indicated for diagnosed cervical cancer. In this case, the woman is treated and observed by an oncologist.
Since PVI is often combined with other sexually transmitted infections, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and other drugs may be prescribed.
Vulgar warts can be removed at home using mummifying agents sold in pharmacies.
Treatment prognosis
Contrary to the belief that the virus remains in the body forever and a full recovery is impossible, doctors give a favorable prognosis. Usually, after a course of therapy, which is developed individually, taking into account the oncogenicity of the virus and associated diseases, the infection recedes.
Relapses do occur, but are relatively rare if treatment is not discontinued. Some people experience a relapse, sometimes several, but shorter and weaker. Continuous exacerbations are typical only for people with a prolonged decrease in immunity due to HIV infection or serious chronic diseases.
Prevention of PVI
Preventive measures are divided into general and specific. General recommendations to avoid infection:
- use barrier methods of contraception;
- have sex with a regular partner;
- do not start sexual activity before the age of 18, since in teenagers the immune system is not yet fully formed;
- Avoid artificial termination of pregnancy.

There is only one specific method of prevention so far - vaccination. Today it is possible to vaccinate against types 6, 11, 16 and 18 of the virus. Vaccination takes place in three stages; it is good to start vaccination in adolescence - from 9-10 years.
Reviews from patients
- "I had condylomas, I didn't know about them, " said the gynecologist after the examination. I immediately asked if we would delete it, I agreed. She then ordered my husband and I to take an antiviral drug. Expensive, but we decided: to undergo treatment until the end. I also made baths with chamomile, string and calendula. Now everything has been clean for two years. "
- "Doctors have different attitudes to treatment. I was diagnosed with grade 1 dysplasia and HPV type 18. One doctor told me - just cauterize, otherwise there will be cancer later. Another said that there is no need to treat anything beforeage 30, especially before giving birth. She only prescribed pills and suppositories. A year later, the virus was still in the test, but two years later it was gone and the cervix was normal. But after 30, asthe second doctor told me, the body no longer heals itself".















